Resistant Starch from Wheat Reduces Postprandial Glycemic Response with concurrent alterations in gut Microbiota
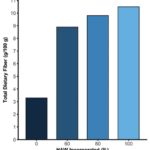
February 2021. Nutrients article: The majority of research on the physiological effects of dietary resistant starch type 2 (RS2) has focused on sources derived from high-amylose maize. In this study, we conduct a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, crossover trial investigating the effects of RS2 from wheat on glycemic response, an important indicator of metabolic health, and the gut microbiota. Overall,…